Implementing Egress Controls
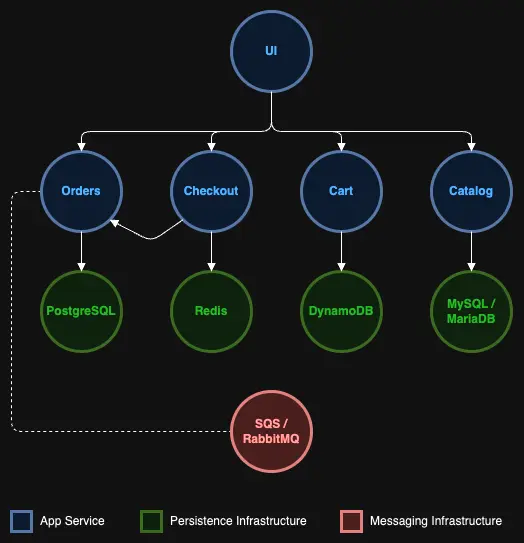
As shown in the above architecture diagram, the 'ui' component is the front-facing app. So we can start implementing our network controls for the 'ui' component by defining a network policy that will block all egress traffic from the 'ui' namespace.
kind: NetworkPolicy
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: default-deny
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels: {}
policyTypes:
- Egress
The empty selector {} matches all pods
The Egress policy type controls outbound traffic from pods
Note : There is no namespace specified in the network policy, as it is a generic policy that can potentially be applied to any namespace in our cluster.
Now let us try accessing the 'catalog' component from the 'ui' component,
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- 0:00:03 --:--:-- 0
curl: (28) Resolving timed out after 5000 milliseconds
command terminated with exit code 28
On execution of the curl command, the output displayed should have the below statement, which shows that the 'ui' component now cannot directly communicate with the 'catalog' component.
curl: (28) Resolving timed out after 3000 milliseconds
Implementing the above policy will also cause the sample application to no longer function properly as 'ui' component requires access to the 'catalog' service and other service components. To define an effective egress policy for 'ui' component requires understanding the network dependencies for the component.
In the case of the 'ui' component, it needs to communicate with all the other service components, such as 'catalog', 'orders, etc. Apart from this, 'ui' will also need to be able to communicate with components in the cluster system namespaces. For example, for the 'ui' component to work, it needs to be able to perform DNS lookups, which requires it to communicate with the CoreDNS service in the kube-system namespace.
The network policy below was designed with the above requirements in mind.
kind: NetworkPolicy
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: ui
name: allow-ui-egress
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ui
policyTypes:
- Egress
egress:
- to:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: service
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: kube-system
The first egress rule focuses on allowing egress traffic to all service components such as 'catalog', 'orders' etc. (without providing access to the database components), along with the namespaceSelector which allows for egress traffic to any namespace as long as the pod labels match app.kubernetes.io/component: service
The second egress rule focuses on allowing egress traffic to all components in the kube-system namespace, which enables DNS lookups and other key communications with the components in the system namespace
Lets apply this additional policy:
Now, we can test to see if we can connect to 'catalog' service:
OK
As you can see from the outputs, we can now connect to the 'catalog' service but not the database since it does not have the app.kubernetes.io/component: service label:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- 0:00:05 --:--:-- 0
* Failed to connect to catalog-mysql.catalog port 3306 after 5000 ms: Timeout was reached
* Closing connection 0
curl: (28) Failed to connect to catalog-mysql.catalog port 3306 after 5000 ms: Timeout was reached
command terminated with exit code 28
Similarly, we can test to see if we are able to connect to other services like the 'order' service, which we should be able to. However, any calls to the internet or other third-party services should be blocked.
Trying XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:80...
* Trying [XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX::XXXX]:80...
* Immediate connect fail for XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX::XXXX: Network is unreachable
curl: (28) Failed to connect to www.google.com port 80 after 5001 ms: Timeout was reached
command terminated with exit code 28
Now that we have defined an effective egress policy for 'ui' component, let us focus on the catalog service and database components to implement a network policy to control traffic to the 'catalog' namespace.